Forgery of signatures and handwriting is common. There are also other ways to forge a document like insertion, obliteration, printing, and so on. Similarly, can a watermark be forged too?
Yes, a watermark on paper can also be forged. The easiest way is by using translucent organic polymers. Other techniques include rubber stamping, printing with chemical inks, and using translucent oils such as linseeds, or photographs.
The following is the table of content for watermarks related to forgery in papered questioned documents.
Why Watermarking is Important in Forensic Forgery Detection?
Watermarks add the ability to detect a forgery in questioned documents by Forensic Document Examiner (FDE). This is how:
- Many forgers are unaware that paper is watermarked— making it easily detectable.
- Some even know about watermarking, but they need to obtain one— unless they get paper, they will not dare to forge documents.
- Finally, what techniques were used to create those watermarks? Each watermarking technique has distinctive identification characteristics.
These three pointers make forging the watermark harder unless they obtain from the original source.
Even if they obtain them from the original source, it opens the door to finding the forger by questioning the person who has access to those watermark sheets. As a result, there is a shorter search group.
Overall, this aids in detecting forgery in questioned documents. Check now: Watermarks on Questioned Documents: Types and Significance
What to do If you Suspect Watermark Forgery?
First, take a quick photo of the whole document. After that, have a close look at the document.
If you think a paper is forged with a watermark, it means there is a higher possibility that the contents of pages are also forged.
So, what to do? First make sure there are no visible changes, alterations, and obliteration in writing on the paper. Then check for the other sign of forgery.
- Alternation in handwriting and signature
- Addition or deletion of clauses in legal documents
- Replacement/addition of the whole page
Soon you identify any above alterations, you should contact the legal authority about the same.
But, if you want to be sure first before filing a complaint, you can hire a private forensic document expert. And, once you’ve obtained surety, you can now contact your legal firm to help you in further preceding.
However, the following are some characteristics that can help you in the determination of water forgery. This can help you to save a couple of hundred bucks in hiring a private FDE.
Table: Genuine Watermark Vs Forged Watermarks
| Features | Genuine Watermarks | Forged Watermarks |
|---|---|---|
| Size and Dimensions | Same size as original | Can be smaller or larger |
| Logo Elements | Fully intact | Minutiae element may be missing |
| Alignment | Specific alignments to the page | Slightly differences in logos placement |
| Opacity | Even | Not even, vary with stamping procedures or chemicals used for forgery |
| Water Absorption | Readily absorb over logo than rest of paper | Even absorption throughout the paper |
| Scent | Paper freshness scent | Chemical, oil, and sometimes unpleasant odor |
| Ultraviolet Light | No marks are seen, and all paper appears the same | Chemically altered absorb UV and have clearly visible lights |
| Fiber arrangements | Displaced fibers | Compressed in stamped, soaked in chemical watermarks |
How to Identify Watermark Forgery on Paper?
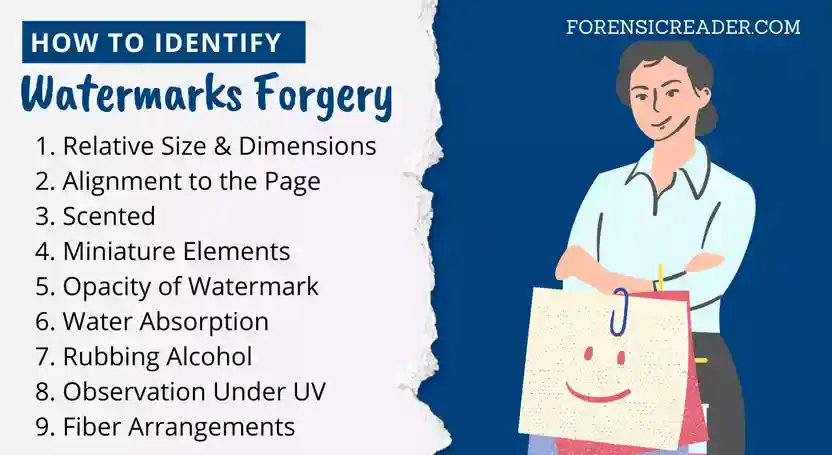
Following are the signs and key characteristics of forgery in paper watermarks.
1. Relative Size and Dimensions
Larger or smaller than the original, with slightly different lengths and width sizes. You can use a scale to trace the dimensions and compare them with the original watermark samples.
2. Alignment to the Page
The majority of forgery involves manual stamping which makes an error window that can be seen as a slightly different arrangement and alignment to the page.
3. Scented
You know the smell of fresh paper. I loved it. I am sure you too love that scent.
Coming to the forensic application; chemically forged paper watermarks use translucent chemicals such as carnauba wax, linseed oil, turpentine, mineral oil, etc. can alter the freshness of paper.
- Smell of carnauba wax: sweet odor
- Flax linseed oil: unpleasant odor
- Turpentine oil: sweet and piney
4. Minutiae Elements
Minutiae characteristics give extra security to replication. They majorly see only with close observation. Many forgers can’t replicate these miniature characteristics and that’s why a remarkable means of identifying genuine watermarks.
Minutiae characteristics can be the
- fiber arrangement
- Microscopic striation lines of rolls
- Unprintable miniature characteristic of the logo itself.
5. Opacity of Watermark
The opacity and translucent factor of manufactured paper are relatively the same. However, up to ± 10% fluctuations are normal because of humidity and temperature. More than that can be a case of forged watermarks. For opacity determination, the most common tool is an opacimeter.
6. Water Absorption
This is a classic test, you can do this at home too. The test is only applicable for the detection of traditionally manufactured watermarks.
- Traditional watermarks: Genuine watermarks absorb water more readily than the rest of the paper.
- Forged watermarks with stamps: Water absorption is even throughout the paper.
7. Rubbing Alcohol
Chemical watermarks that use organic translucent chemicals can be detected by the application of ethanol.
Is it destructive? Yes. Did it work? Hell, ya.
If you simply want to know whether the paper you have is manufactured with a traditional watermarking method or not, you can use rubbing alcohol.
- Genuine Traditional Watermarks: the watermark is visible even after the application.
- Chemical Watermarks: losses the watermarking.
8. Observation Under UV
You need a UV torch. It may be hard to find online but if you have it, this is what you will observe.
Chemical watermarks under long UV appear darker. Conversely, watermarks under short UV appear more translucent and lighter. While traditionally manufactured marks under both long & short UV remain even opaque.
Why? Because…..translucent chemicals of watermarks absorb these UV rays and appear lighter/darker.
P.S. I suggest only using long UV, as it is less hazardous. But short UV gives more distinctive observation.
9. Fiber Arrangements
All the above methods state the difference in how traditional watermarks are different from chemical ones. But with fiber arrangement examination, you can differentiate between traditional watermarking and stamped watermarks.
Paper watermarks are majorly forged by stamping design over semi-wet or dry paper. On the other hand, traditional genuine watermarks are made by punching the design on wet sheets resulting in fiber displacement from their position.
But in the case of forged traditional paper watermarks, the translucent design is made by compression of dry sheets.
In short, artificially stamped watermarks have a compressed design while true watermarks have displaced fiber arrangements. Check how fiber and pulp analysis help in determining the paper forgery.
A quick tip: For this, you may require a microscope. In case you have that, it’s good. Otherwise, you can use a scanner with 1000dpi (but observation quality is not good) and zoom to the max to observe.
Please Note: The above observation is an overview that detects forgery in the majority of cases. However, it can’t state a watermark genuine to 100%. For that extensive analysis of watermarks should be done. You can check out the dedicated post: Watermark Examination on Paper.
Detection of Watermark Forgery on Paper Using Watermark Detectors
There are two common Watermark detectors; one uses alternative light sources and the other is a liquid solution.
A. Optical Watermark Detectors Instrumental Tool
The two most common ones are;
- Lighthouse Sherlock Watermark Detector
- SAFE Signoscope T1 Watermark Detector
Principle of Optical Watermark Detectors Tools
Documents such as bond paper, security notes, stamps, and banknotes can be detected by these detectors.
Why only these? Because they have multi-colors that shine differently in alternative light produced by optical watermark detectors.
As traditionally manufactured watermarking doesn’t have different shades of color, thus these detectors can’t aids in their examinations.
Disadvantages of Using Watermark Detector in Examination of Paper Watermarks
- Very small analysis window usually 6×6 cm.
- Can’t differentiate between traditional and stamp paper watermark forgery.
- Limited color spectrum for analysis (white, red, green, and blue).
- For paper analysis, watermarks need to be cut and if the sample is limited, the examiner can’t afford to destroy evidence on analysis that can be examined non-destructively.
- Not used by Forensic Document Unit (FDU) as they majorly have a full-scale alternative light system that can examine the whole sheet at once.
- Banknotes and security bonds are financial papers, if found genuine, their parting may lose their admissibility for future services.
That’s too many disadvantages! Should I buy a watermark detectors tool like Lighthouse Sherlock or SAFE Signoscope T1 Watermark Detector?
Yes, but only one when you need to examine stamps. Plus, they are the best most portable means of examining genuine stamp watermarks.
Features that can be seen using watermark detectors and instrumental tools:
- very much every shade
- Paper irregularities
- Quality defects
- Reveal signs of repair or alteration
- Adhesive markings
B. Watermark Detector liquids
These special liquids are first applied (or soaked in) to the watermarks and let it diffuse. As a result, it makes watermarks more translucent and shaded.
This reveals a clear image of the watermark design. You can closely relate it to the application of rubbing alcohol on chemical watermarks.
In the USA, the most commonly used watermark detector liquid by stamp examiner or collector for authentication is Super Safe and Charity liquid detectors.
They are labeled as quick-drying, non-toxic, grease-free, and non-flammable which would not alter the shades and watermark of stamps.
How Forger Forged Watermarks on Paper?
Some of the common methods of watermark reproduction can also be used for forensic documentation.
1. Manual Tracing and Rubbing
Tracing it under transmitted light. Time-consuming and may cause indentation over the original paper. While rubbing is extremely outdated and used only for embossed raised watermarks.
Both methods are very subjective and not commonly used by pro-forger.
2. Ilkley Method
Developed by Robin Alston in 1976 and uses two glass arrangements that sandwich a photographic film and watermark. This arrangement exposed for 5 seconds in visible light results in replication of the watermark design.
3. Photosensitive Paper
Similar to the Ilkley method. A phosphorescence watermark uses a phosphorescent pigment plate, a blue-sensitive photographic film, and illuminating source of UV and IR.
IR rays make the phosphorescent pigment plate to be dark. UV rays, on the other hand, glow only in the watermark area. This combination makes a clear and crisp image of the watermark.
The setup is first illuminated for 10 seconds with UV light followed by IR for 10 seconds from a 10cm distance.
4. Printing Chemicals on Paper

Translucent chemicals such as Polyethylene glycol, disaccharides, etc. are common elements of chemicals that can be used to make a duplicate copy of a watermark that looks original. Check different types of translucent chemicals used in chemical watermarks.
These chemicals are placed in printer cartridges that print the computerized design right over the paper.
5. Rubber Stamping
Just hit the rubber stamp on the paper with ample pressure, and you got a watermark. But they are temporary and can easily be eliminated with too much handling.
However, using rubber stamping with translucent chemicals can replicate nearly the same marks as the original.
Moreover, there is also a very similar manufacturing technique called stamp roll watermarks. They have a dandy roll-raised design and drum arrangements. In this, semi-dry paper is sandwiched between the arrangement resulting in permanent watermarking.
Both have compressed watermarks but stamp roll watermarks are more deep and translucent because they use semi-dry paper.
The key difference between original stamp roll marks and rubber stamp marks:
- Stamp roll watermarks have crisp and sharp edges.
- Usually have characteristically stamping lines on dandy stamp rolls paper.
6. CCD With Back Lightning
It is easier, quicker, and produces a good quality of reproduction without the need for any sophisticated equipment.
Equipment Needed:
- High-resolution digital CCD (Charge Coupled Device)
- Light source or lightbox (thin homogeneous lighting behind the paper)
Techniques use CCD cameras to capture reflected (from the front) and transmitted (back-light) images of the watermarked paper. This is the first step to getting a watermark design with minutiae details
7. Thermophotography
Relatively newer techniques were developed by Neuhauser in 2005.
Equipment needed:
- Infrared light
- Warming plate
The science behind this is infrared cameras are sensitive to thermal radiation that is placed behind the watermark. The thermal radiation plate maintains the temperature between 35° to 40°C. The thermal-sensitive IR camera captures all the changes and produces a digital watermark image.
Cautions: distance of the thermal plate should be 1cm with 1 sec of exposure time. More closeness or exposure results in the destruction of paper.
8. Radiography
Grenz Process uses soft X-ray illumination for producing watermarks. The watermarked document is placed between a soft X-ray source (rays at 7kV) and an X-ray film.
Another method involves the use of a beta-isotopes plate. The X-ray is illuminated from the beta-isotope through the paper to produce the watermark image on the X-ray film.
Both methods produce exact replication with minimum interference. But production cost is high and also time-consuming.
General FAQs
When is watermark forgery common?
Watermark forgery commonly involves altering watermarks on documents related to disputing property, bonds, wills, checks, banknotes, certificates, addition or deletions of clauses, or special terminology from proprietary terms.
How to prevent watermark forgery?
You can’t make a watermark 100% secure. But you make it harder to trace the design, eg: using minutiae characteristics that are harder to replicate or engraved.
Can watermarks be removed from a paper document?
No, you can’t 100% remove a watermark from paper, not even the chemical ones. Even if they are visibly removed, when they observe under short and long UV rays, they reappear clearly. However, you can document and replicate the exact image from paper using photographic development techniques.
What are the limitations of watermarking examination in forgery detection?
They are harder to differentiate because due to the new modern development and imaging process, finding differences between genuine and forged watermarks are very less.
Continue Reading:
- 14 Myths of Fingerprints And Questioned Documents: A Forensic Study
- Paper Dating Using Watermarks: Is It Possible? Forensic Analysis
- Watermarks on Questioned Documents: Types and Significance
- Forensic Watermark Examination of Paper: Destructive And Non-Destructive Analysis

FR Author Group at ForensicReader is a team of Forensic experts and scholars having B.Sc, M.Sc, or Doctorate( Ph.D.) degrees in Forensic Science. We published on topics on fingerprints, questioned documents, forensic medicine, toxicology, physical evidence, and related case studies. Know More.
