What is FPLMN?
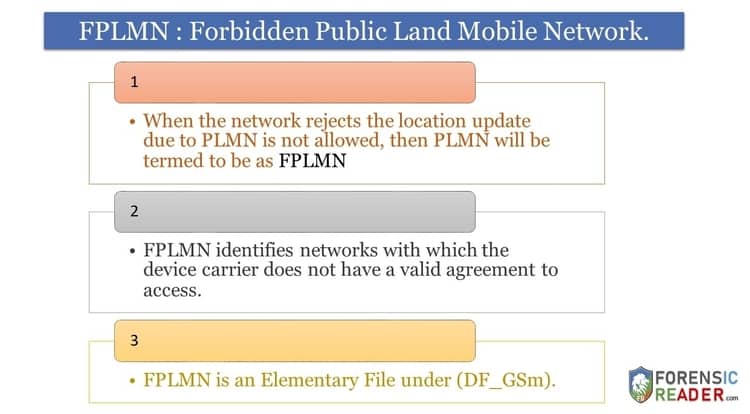
FPLMN in telecom stands for Forbidden Public Land Mobile Network. It is an Elementary File under the DF structure for GSM (DF_GSm).
FPLMN helps to identify networks with which the device carrier does not have a valid agreement to access.
The PLMN will be termed to be as FPLMN when the network rejects the location update due to PLMN is not allowed.
FPLMN – Future Public Land Mobile Network
Sometimes FPLMN also stands for Future Public Land Mobile Network.
Here the term “Future” is related to the development of networks in the telecom industry.
These may be fifth-generation networks or sixth-generation networks.
Uses of FPLMN
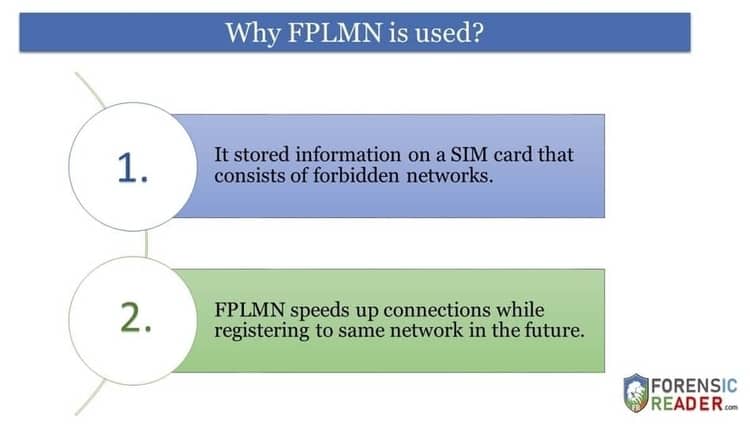
As we know FPLMN is a list of stored information on a SIM card that consists of forbidden networks.
Generally, traditional modems save networks to the FPLMN list after failed attempts at registering onto them.
The main reason to save this list is to speed up connections while registering to the same network in the future.
Process of Data Retention of FPLMN
FPLMN Elementary File earlier days can save up to four records and when this record is full then the new data is get written on the first recorded one.
But the new UICC specification extends this limit up to n records which further depends and varied by the card manufacturer and corresponding carrier specification.
Irrespective of the manufacturer, each card has a limit to the number of FPLMN records to hold up.
At the point when a record is added to the FPLMN Elementary File, then by default, the record is set after the last record.
But if there are no extra slots available, then the first record is expelled out and the new record is added to the last available slot.
Example of Information on FPLMN Earlier File System
- Length (Bytes):12 bytes
- Bytes distribution :
- 1-3 bytes = PLMN 1
- 4-6 bytes = PLMN 2
- 7-9 bytes = PLMN 3
- 10-12 bytes = PLMN 4
As seen above in the earlier introduction of FPLMN it seems that each record i.e. PLMN 1, PLMN 2, PLMN 3, and PLMN 4, has required 3 bytes of data to store their respective information.
Forensic Importance of FPLMN
Strictly talking to the forensic aspects, an FPLMN is useful for the examiner in the following ways:
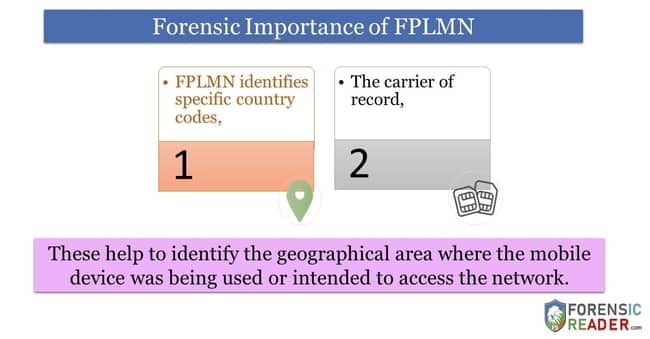
- FPLMN identifies specific country codes, and also
- The network carrier’s record,
This help to identify the geographical area where the mobile device was being used and intended to access the network.
Related Article:
1. Mobile Device Forensic: Ultimate Guide for Collection
2. Mobile Forensic Data Acquisition Methods and Tools
A Short Overview of PLMN
PLMN stands for Public Land Mobile Network. It is a defined area, to which the mobile operator has access to a service provider for voice and data services in that specific area.
When a PLMN connects to other PLMN networks in order to provide voice and data services then it charges the roaming services.
In other words, if you migrate to a different state then your previous state PLMN networks get interconnected to the newly migrated area to serve you their services.
A PLMN has a unique identifier called a PLMN identifier which has a globally unique code.
It consists of MCC (Mobile Country) and MNC (Mobile Network Code). It is a five to six-digit number which identity:
- A country, and
- Network Operator
Example: 310-06 or 310-038.
Here, “310” represent the country, and “06” or “038” represents the corresponding network operator or provider of that country.
Related terms to FPLMN (PLMN)
HPLMN
HPLMN is abbreviated for Home Public Land Mobile Network.
It identifies the PLMN in which the subscriber’s profile is configured (or we can say that the local place from where it (SIM) is brought to).
When the users migrated or travel to other regions (a roaming area) then it receives subscription information from the HPLMN.
VPLMN
VPLMN stands for Visiting Public Land Mobile Network.
It can be defined as when a subscriber is roaming and attaches to the roaming core network via the access network.
Then, this Roaming core network belongs to a PLMN which can be called VPLMN.
UPLMN
UPLMN stands for User Public Land Mobile Network. It belongs to user priority i.e. which PLMN the user wants to connect and its priory is set by the user alone.
OPLMN
OPLMN stands for OperatorPublic Land Mobile Network. The just opposite of UPLMN, here the PLMN priority is set by the mobile provider.
IPLMN
Interrogating Public Land Mobile Network abbreviated form of IPLMN. As per the name in this PLMN, there is a process of interrogation. It serves the two-step process:
- When a dialed subscriber the call first directed to GMSC: Gateway Mobile Switching Centre
- Then interrogation comes into the role: In GMSC the call is interrogated for further call routing.
EPLMN
EPLMN stands for Equivalent Public Land Mobile Network. Here is a shift in the services provider with charging the roaming due to the unavailability of the native service provider or operator.
Example: The two network providers A and B in a country.
Network provider A has unavailability in some states but Network provider B has access to it, so in that case Network Provider B serves the user without any extra roaming charges, only if both companies agree to it.
Bottom line of FPLM-SIM
Forbidden Public Land Mobile Network (FPLMN) helps to identify networks with which the device carrier does not have a valid agreement to access.
The FPLMN list helps the device speed up connections while registering to the same network in the future.
And for the forensic prospectus, specifies the country code and also operator provider details to invade the case in mobile forensics.
Apart from FPLMN, there are other PLMN files such as UPLMN, OPLMN, HPLMN, VPLMN, EPLMN, IPLMN which is described in this article.
If you like this concise post on “FPLMN (SIM): A detailed Explanation | UPLMN, OPLMN, EPLMN, HPLMN“, then share your love in the comment box, we love to hear from your side.
Related Article:
1. Mobile Device Forensic: Ultimate Guide for Collection
2. LOCI SIM Forensic Analysis
3. Mobile Forensic Data Acquisition Methods and Tools

FR Author Group at ForensicReader is a team of Forensic experts and scholars having B.Sc, M.Sc, or Doctorate( Ph.D.) degrees in Forensic Science. We published on topics on fingerprints, questioned documents, forensic medicine, toxicology, physical evidence, and related case studies. Know More.
