Is it possible to Find Fingerprints on Human Skin and Body? When and When Not?
Fingerprints can also be found on human skin but many forensic experts believed their development to be a challenging task. They are usually latent (not seen naked eye), and rarely visible (from blood, dirt, paint, etc.) marks.
Though skin is a common substrate on which fingerprints can be found but their need for forensic purposes is not common. It is commonly seen in violent cases. The following are the most common places where fingerprints can be found.
| Cases | Body Parts Where Prints can be Found | Fingermarks Type |
|---|---|---|
| Strangled | Neck, chin, face | Fingers & partial palm prints |
| Assault | All over body (thighs & forearms common) | Fingers & palm prints |
| Slapped | Face | Mainly fingermarks |
| Touched | Any body part | Fingertips marks |
The chance of getting fingerprints over a live body is much less than that of a dead body. The recovery rate of fingerprints from cooled (4˚C) dead bodies is excellent while the rate on a warm dead (37˚C) body is intermediate and for living it is poor.
However, in the case of prints from blood, grease, oil, body lotion, etc there is a higher chance of getting fingerprints even on living human skin.
How long do Fingerprints Stay on Human Body and Skin?
If a person’s body is alive, fingerprints on human skin stay about 4 hours [Trapecar, 2009] before being damaged by body fluids like natural sweat, oil, or skin elasticity. After death, there is seize of secretion of body fluids and skin elasticity, allowing for a longer development time of 4hrs in a warm cadaver and 16 hrs on a cold body (at 6°C) [Hébrard and Donche, 1994].
Another study by Adcock (1977) concluded that prints can be developed for up to 2 to 5 days on cadavers.
In a general scenario, the fingerprints can last as long as they are not destroyed and the skin constantly regenerates. Thus, the chance of finding prints may become less and less as time passes. So, it is crucial to develop fingerprints asap.
Factors Affecting Finding Fingerprints on Human Skin
1. Types of Fingermarks: Fingermarks made from oil, grease, lubricant, blood, paint, etc tend to retain longer time than simple sweat fingermarks.
2. Dead vs Living: Fingerprint can’t remain intact for a longer time as compared to a dead body because in living contact skin regeneration and skin porosity destroy the marks over time.
3. Pressure of Application: When pressure is applied to softer tissues such as the neck, the force of constriction from the hand causes a bruise that not only imprints the size of the hand but also fingermarks with much higher details than regular touch.
4. Body Parts Involved: Non-stretchable parts such as the forehead, and cheeks tend to retain fingermarks for longer periods of time than other parts of the body. Other factors such as relatively smooth, hairless, and clean areas of skin facilitate development.
5. Temperature and Humidity: In winter there is less sweating than in summer which decreases the chance of destruction of fingerprints by sweating.
6. Biochemical Functions: Body sweat and oil secretion are examples of biochemical functions. Fingerprints do not remain on the skin longer on skin that secretes more sweat or oil.
7. Skin Texture: Skin texture can be normal, dry, or oily. Dry skin tends to have better ridge details when made from external oil, dirt, etc. For oily skin, ridges are better when they are made from both dry fingers or with external oil, dirt, etc.
8. Skin Elasticity: The skin is elastic so naturally the elasticity distorts any static fingerprints present on the skin.
Male Vs Female Skin: Which Has a Higher Chance of Getting Fingerprints?
According to the study published in the International Journal of Female Dermatology, the skin parameters such as hydration, transepidermal water loss, microcirculation, and thickness are generally higher in men as compared to women.
This means, there are higher changes in terms of the production of natural sweat and skin texture in men this can imply that the chance of getting fingerprints on female skin is higher than on males. Again, it varies from case to case.
Read More: 47 Branches Of Forensic Science: Disciplines And Division With Evidence And Case Types
Ways to Finding Fingerprints on Human Skin
In forensics, there are various means of finding fingerprints on non-living substrates. When dealing with the skin, one should acknowledge the damaging power of various alternative lights such as UV. So, in any case, one should avoid these means of detecting fingermarks.
Following are some of the methods of finding fingerprints:
- A bright light source at an oblique angle.
- Alternative Lightening without using UV spectrum (must be avoided on living skin).
- Light laser can be used (but avoided on living skin because it might cause skin regeneration).
- Infrared photography: imaging blood spatter or injuries bruising on the skin.
- Electronogprahy (X-ray): only on dead skin. It enhances the image and removes the background on the skin texture, hair, etc.
Methods of Developing Fingerprints on Human Skin
Following are the proposed methods for developing fingermarks on Human Skin:
| Method | Procedure | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Powdering | Magnetic Jet Black and Swedish black are used to dust overprints using a fingerprint brush on the skin. | Skin surface needed to be completely dried otherwise high background development. |
| Direct Transfer | Transferring prints from skin to another surface such as glass, or glossy paper, before developing | Transferring prints removes the skin background and better contrast. |
| Iodine-Silver Plate Transfer | Fumed with iodine vapors, then pressed against a silver plate then exposed to 5-10 secs under direct sunlight or UV lamps. | Dark brown prints formed on silver plates. |
| Cyanoacrylate | Treated with CA in the fuming chamber or fuming tent. | Ridges can be directly photographed or treated with rhodamine 6G or BY40. |
| Ruthenium Tetroxide (RTX) | Treated with RTX as vapor or as a solution. | should be applied in sequence, after iodine fuming. |
Sequence of Developing Fingerprints on Human Skin
Following is the sequence of detection and development of fingermarks on human skin.
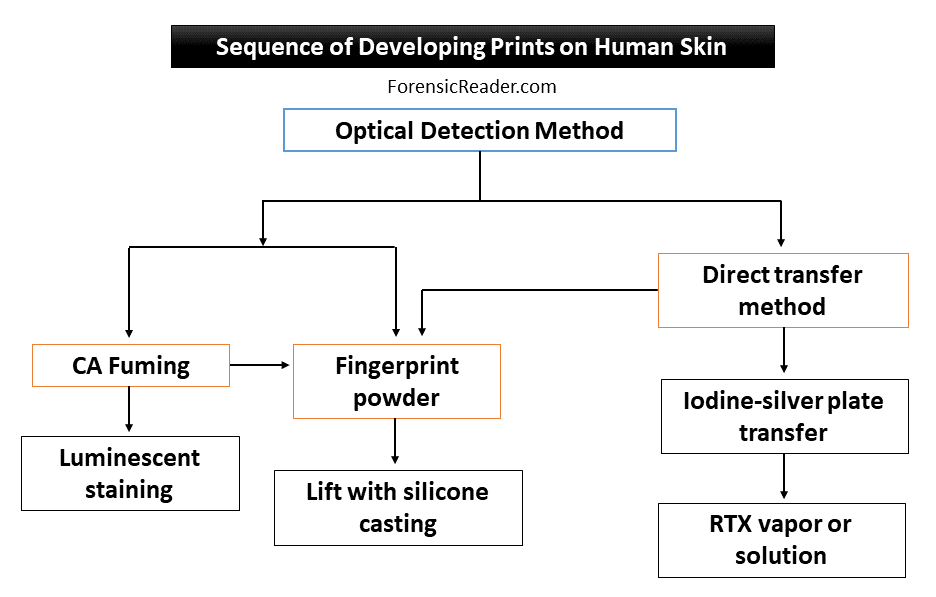
Photographing Fingerprints on Skin
Fingerprints present on the skin cannot be visible to the naked eye. So it also cannot be photographed without first developing. At first, the latent fingerprints should be developed using various methods in the proper sequence that was discussed earlier.
After that using oblique lighting of proper filters should be used at a close range and midrange photographs of developed fingermarks.
Can fingerprints be lifted from Human Skin?
Yes, fingerprints can be lifted from human skin. They are first needed to be developed and then lifted by various lifters. However, it is not advisable to lift developed fingermarks by fuming methods such as iodine, RTX, and CA.
| Lifters | Lifting Developed Prints |
|---|---|
| Transparent instant lifter (BVDA) | More suitable |
| Microfilm for micro trace | Poor |
| White/Transparent gelatin foils | Best |
| Transparent adhesive tape | Poorest |
| Silicone casting material (Isomark®) | Best |
A new technique called kromekote lift technique is proven to be effective in lifting marks from human skin. Procedure: Kromekote card (a high gloss paper) is placed on developed fingerprints, pressed, and then lifted.
Best Practice and Sequence: Prints developed using magnetic powder→photography→lifters.
Is it possible to extract DNA from Fingerprints on Human Skin? And how long?
The possibility of getting DNA from fingerprints on human skin is very less. This is due to contamination from the substrates of human skin. Other factors such as the regeneration nature of skin (in living individuals) and development techniques have also proven to be governing factors in developing prints.
However, factors such as blood, soft tissue, saliva, etc also proven to be advantages of getting DNA. In general cases, one-third of the samples powdered with black powder can result in a better success rate of getting full DNA profiles.
References:-
- Fingerprint recovery from human skin surfaces [Pubmed]
- Latent Fingerprint on Human Skin: A Silent Diagnosis [Researchgate]
- Methods for detection of latent fingerprints from human skin [EuropePMC]
- Identification of Fingerprints Left on Human Skin by Shin, D.H. and Argue [Tandfonline]
- The development of latent fingerprints on Human skin: The iodine-Silver plate transfer method by Adcock, J. M. [OJP.Gov]
- Fingerprint Detection Methods on Skin[Ojp.Gov]
- Lifting techniques for finger marks on human skin previous enhancement by Swedish Black powder–a preliminary study [Nih.gov]

FR Author Group at ForensicReader is a team of Forensic experts and scholars having B.Sc, M.Sc, or Doctorate( Ph.D.) degrees in Forensic Science. We published on topics on fingerprints, questioned documents, forensic medicine, toxicology, physical evidence, and related case studies. Know More.
