Forensic Hair Sample Analysis using NAA and AAS
Both neutron activation analysis (NAA) and atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) are used to estimate the concentration of arsenic in biological samples such as hair, nails, and bone. These techniques are highly sensitive and can detect trace amounts of arsenic. A. Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA) Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA): NAA is a nuclear process used for determining […]
[Table] Historical Development of Fingerprints
Year Individual/Organization Contribution 3000 BC Masons Used finger impressions on brickwork for projects for kings and pharaohs. 500 BC China and Babylon Imprinted clay tablets and business records with the author’s fingerprints for identification. 1684 Nehemiah Grew Published the first written description of fingerprints in the West, including detailed drawings. 1686 Marcello Malpighi Described ridges, […]
Forensic Sciences Institutions (CFSLs, SFSLs, GEQD, CFPB, NFSU)
Part 1: Famous Forensic Institutions NFSU Campus Here is the list of campuses with their total departments (last updated on Feb 2024). Learn More.-> Department (1): Pune, Guwahati and Manipur-> Department (2): Goa, Tripura, and Bhopal-> Department (3): Dharwad and Uganda-> Department (6): Delhi-> Department (16): Gujarat Part 2: CFSLs under DFSS (Details of CFSLs) Part 3: State FSLs State City […]

Soil as Evidence: How Soil Helps in Solving Crime and Forensic Significance
Forensic pedology or soil forensics is a branch of forensic science that focuses on analyzing soil as trace evidence in criminal investigations. It involves studying soil properties, including texture, color, and chemical composition, to connect suspects, victims, or objects to specific locations. In addition, analyzing soil layers can aid in pinpointing crime sites, burial sites, […]

Forensic Fiber Analysis and Chemical Tests With Case Studies
Fibers are a valuable type of evidence in solving cases. They can be used to identify suspects, victims, and location of crimes. The steps involved in processing fiber evidence include recovery, identification, comparison, and evaluation. In all, one of the essential aspects of forensic analysis is the examination of fibers found at crime scenes. Chemical […]
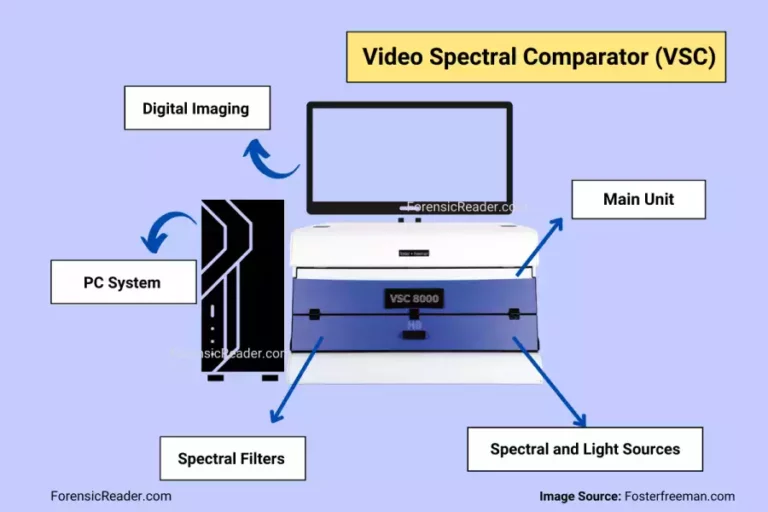
Video Spectral Comparator (VSC): Principle, Parts, Uses, Advantages and Disadvantages
The Video Spectral Comparator (VSC) is a UV-Vis-IR imaging spectral device designed for forensic examination and authentication of questioned documents. It was developed by Foster and Freeman. A basic VSC unit consists of a high-sensitivity camera, different light sources, a software/viewing interface, and a positioning stage. The built-in multiple spectrum sources can reveal hidden characteristics […]
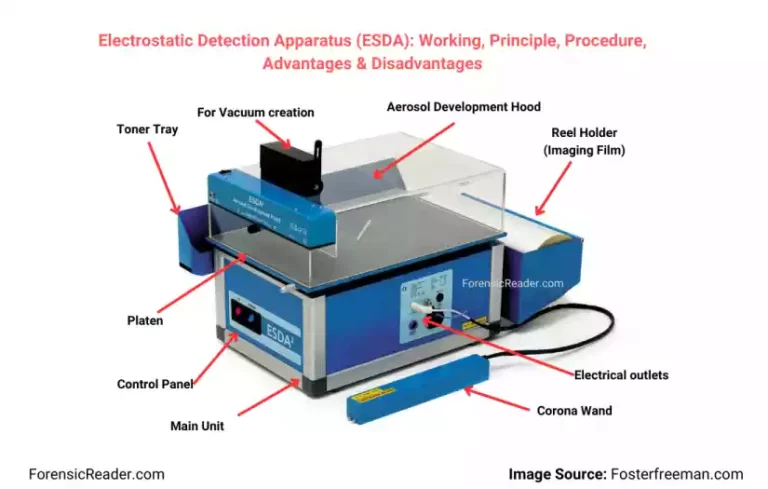
Electrostatic Detection Apparatus (ESDA): Working, Principle, Procedure, Advantages & Disadvantages
Electrostatic Detection Apparatus (ESDA) is an electrostatic detection device (EDD) specifically made by Foster and Freeman Ltd. to reveal indented writings on a paper surface. With time, ESDA become synonymous with EEDs for detecting indented writing or marks on forensic questioned documents. Moreover, it offers a non-destructive nature of detecting indentation because it operates on […]
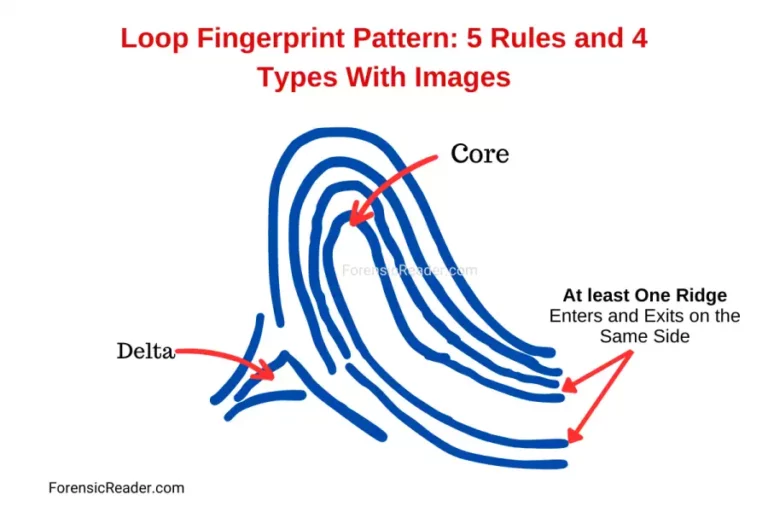
Loop Fingerprint Pattern: 5 Rules and 4 Types With Images
Loops are the most common fingerprint patterns, accounting for 60%-70% of all patterns, where ridges enter from one side of the finger, make a U-turn around a central point (core), and exit on the same side of the finger. This characteristic U-turn of the ridge is called a “recurve”. However, all U-turn patterns are not […]
