Once the device is found, the main aim of it is to extract useful data that can direct the case to its end. This article emphasizes the various forensic mobile data acquisition techniques and tools and their methods used in digital mobile forensics.
What is Forensic Data Acquisition and Tools?
Forensic data acquisition is defined as creating a forensic copy to extract useful information that is stored in a digital device using various mobile forensic tools.
Forensic Data acquisition starts with creating a forensic image copy using the desired copy then all the work of extracting data is from the image file. It serves two purposes:
- It maintains the integrity of original digital evidence.
- Preserve the evidence as proof of its original copy
Types of Forensic Data Acquisition Tools
In mobile forensics, there are basically two types of data collection techniques i.e.
- Logical Acquisition of data
- Physical Acquisition of data
Logical Acquisition of Data
A logical data acquisition is the extraction of the user’s data from a mobile phone using forensic tools without touching the device’s file system.
In 2014, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), “Guidelines on Mobile Device Forensics,” described it as imaging of logical storage of devices (such as directories and files) that reside on a logical store (such as a file system partition).
Physical Acquisition of Data
NIST SP 800-101 states that a “physical acquisition implies a bit-by-bit copy of an entire physical store (e.g., a memory chip)”.
It is a type of data collection that includes system files, application data, and other information, that is not accessible to the user via the GUI of the device.
It can be considered as the complete representation of data stored in the actual mobile flash devices or other storage devices but forensic tools like encase, etc for creating an image file.
This type of data acquisition tool method implies direct communication with a device’s internal data storage to collect the stored data.
Non-Invasive Physical Data Acquisitions
According to SWGDE, “Non-Invasive Physical Collections involves a process that provides physical acquisition of a phone’s data without requiring opening the case of the phone.”
In this method, the data stored in a mobile device are visible by the communication method using various ports mainly USB ports or FBUS connections.
The data collected by the non-invasive technique is not a bit-by-bit representation of the entire device memory store.
Example:
- A flasher box to a device’s USB port or FBUS connection.
- Using tools such as Oxygen Forensic Analyst or Detective, UFED, etc.
Invasive Physical Data Acquisitions or Collections
According to SWGDE, “Invasive Physical Collections involves a process that provides physical acquisition of a phone’s data and requires disassembly of the phone for access to the circuit board.”
In other words, it can be seen as the acquisition of data from a mobile device via access to its memory chips and circuit boards.
Example of mobile forensic tools:
- JTAG (Joint Test Action Group): JTAG allows for communication with the device processor to access the NAND area of the device and obtain a binary file containing a representation of the partitions on the device.
- Chip-off: It is the removal of the memory chip from the mobile device, and reading using specialized hardware and software.
Related Article:
1. Mobile Device Forensic: Ultimate Guide for Collection
2. FPLMN (SIM): A detailed Explanation | UPLMN, OPLMN, EPLMN, HPLMN, IPLMN, VPLMN
File System Data Acquisition
It is termed a collection technique that bridges the gap between a logical extraction and a physical collection.
A file system collection contains considerably more information than the defined logical collection methods.
A file system is defined as the collection of files and folders that the device uses along with already installed applications, system configurations, user configurations, and user storage areas (media files, documents, zip, and other formats).
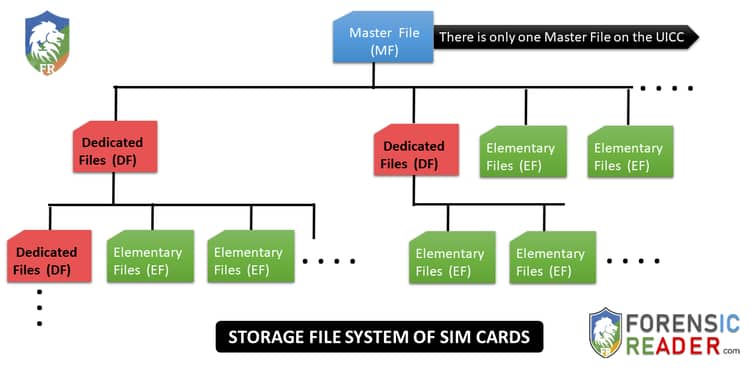
Types of Files System Data Collections protocols
- USB Mass Storage Class (MSC):
MSC transfer protocol allows the user to mount the devices as a storage area.
It provides direct access to data sectors for the reading and writing process. Most of the primary forensic aspects for a mobile device are focused on MSC partition devices. - Picture Transfer Protocol (PTP):
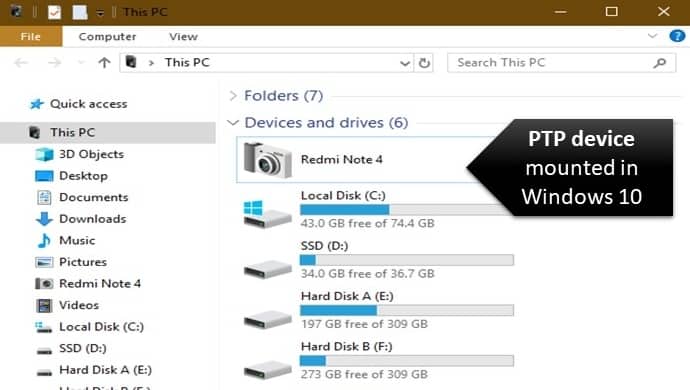
PTP is one of the widely supported protocols that is standardized by the International Imaging Industry Association.
This protocol enables the forensic expert to extract the images and videos from PTP-mounted devices to computers without the use of any third-party applications and mobile forensic tools:- PTP only deals with Images and videos and their corresponding metadata.
- It doesn’t support the transferring of other file formats example zip files, word documents, and so on.
- It is unidirectional in nature i.e. one can only download or copy files from the PTP device to the computer but does not support uploading or transferring files to the device.
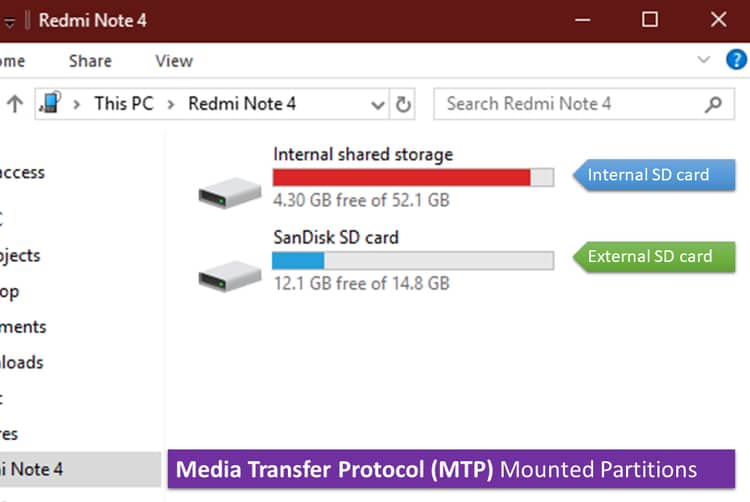
- Media Transfer Protocol (MTP):
It can be called as a subset of Picture Transfer Protocol (PTP) with additional enhancements and enables communication. It was introduced to improve the PTP protocol by Microsoft which is not limited to only media files but any type of file can be transferred. - It is bidirectional i.e. files are transferred to and from the mobile mounted using MTP protocol. MTP emphasizes the importance of metadata associated with media files, just like PTP does with images.
Mobile Device OSs and Data Accessible Using PTP and MTP
| Operating System | Type | Type of Data |
| Apple iOS | PTP | Images and videos |
| Android, BlackBerry 10, Windows Phone | MTP | Images, videos, and media (documents, files, other) |
Mobile Data Collection Pyramid (Acquisition Method & Forensic Tool)
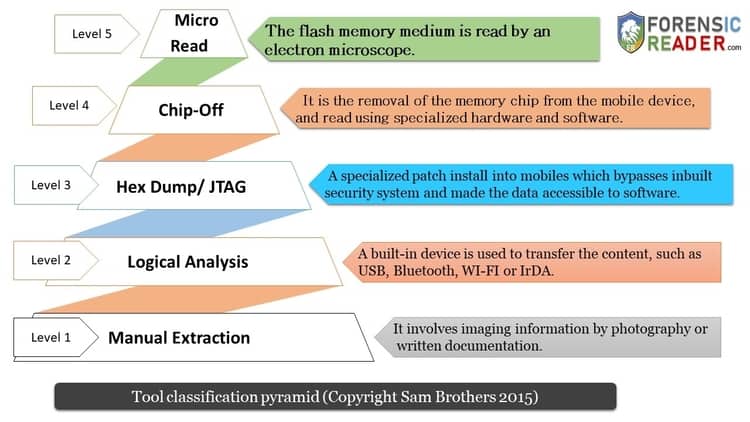
Phase 1: Manual extraction
Manual extraction, or examination, involves imaging information by photography or written documentation.
Conducting a manual examination by means of the “commando method” or by “thumb jockeying”, which involves manual manipulation of the device to extract evidence stored inside.
Phase 2: Logical Analysis
This is one of the most widely used data extraction methods in mobile forensics as well as forensic software vendors. In a logical extraction method, a built-in device is used to transfer the content, such as USB, Bluetooth, WI-FI, or IrDA.
The built-in features are used to make a connection between the device and software that is used to extract data using commands comprehended by the mobile device.
Phase 3: Hex Dumping/JTAG
It is just like the Trojan horse software. In this extraction method, a custom specialized software, package, or ROM is made to install into the volatile memory of mobile devices. In doing so, it bypasses the inbuilt security system and makes the data accessible to this specialized software.
Example: iPhone data can be extracted using this method as they have encrypted internal storage data sectors.
But devices having chip-level encryptions still don’t resolve using this data extraction technique.
The JTAG with a mobile device using the device TAPs (Test Access Points) gives the examiner access to the flash memory and the output is in a binary file of the desired selected partition or storage area.
JTAG ought to be an invasive way of extraction technique as the device is disassembled and in some instances, it gets directly soldered to the TAPs on the circuit board.
Using these specialized tools which comprise hardware and software, the examiner uses this software to communicate via hardware to the microprocessor of the device that interfaces with the flash storage device.
Phase 4: Chip off
The chip-off examination involves the physical removal of the mobile device’s flash memory. Using specialized tools and techniques, the examiner disassembles the device and removes the flash memory from the circuit board. It is one of the handy data acquisition mobile forensic tools.
Once the flash module is removed intact, it is placed into a specialized component to read memory modules.
A chip-off examination is invasive. And once the chip is removed from the device, the chip would need to be reballed and then reinstalled into the device so it could operate as it had previously. This process is extremely labor-intensive and equally expensive.
Level 5: Micro Read
In this level of examination, the flash memory is read by an electron microscope. This type of examination is not only considered theoretical but it has never been conducted publicly on mobile device evidence.
The theory involves using an electron microscope to read and count electrons that occupy a cell on a flash memory chip. If electrons are present, it is represented as “1”; if no electrons are present, it is represented as “0”.
This is often referred to as “gating.”. After combining the binary data, it can be translated into raw data and interpreted.
Related Article:
1. How mobile device used in a crime?
2. LOCI SIM Forensic Analysis
3. Tim Lloyd & Omega Engineering Inc [Hack Attack] Forensic Files Case Study
Bottom line
At last, if you find this concise article “Mobile Forensic Data Acquisition Methods and Tools“, then don’t be harsh on us and share your love in the comment box, we love to hear from your side.

FR Author Group at ForensicReader is a team of Forensic experts and scholars having B.Sc, M.Sc, or Doctorate( Ph.D.) degrees in Forensic Science. We published on topics on fingerprints, questioned documents, forensic medicine, toxicology, physical evidence, and related case studies. Know More.
