Color Coding bullets are one of the visible markings on the tips of the bullet that define the category and origin of these ammunitions. But, let’s start with one of the basic questions.
What Bullet Tip Color Codes Means?
Color-coded bullet tips are used to categorize and identify various types of military ammunition. These colorful bullet tips are not found in civilian ammo. And they are visible as a single color or multiple color bands across the bullet nose.
However, a slightly different color-coding system is also seen on the joints between the primer and cartridges case (primer annulus).
As stated earlier, bullets with color codes, usually signify that it is military ammunition. And the majority of standard bullets don’t have any color code.
So, if a bullet has no varnished color, in military nomenclature, it is called to be the standard bullet round or standard ball rounds.
Color-Coded Bullets Tip Tables
Different Types of Color-Coded Bullets and Their Meaning
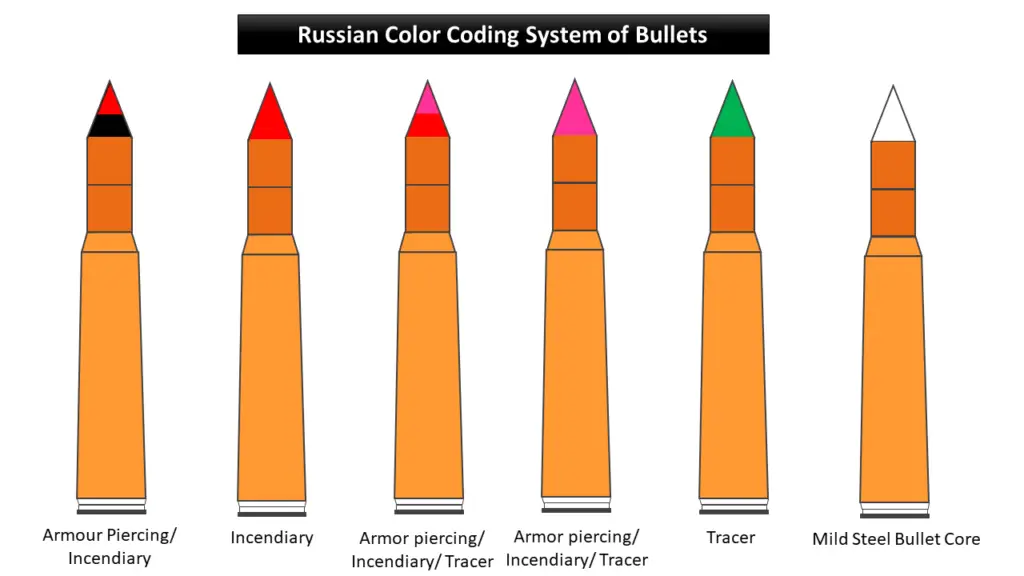
Russian Color Coding System of Bullets
The following table is the color-coding bullet (tip) list that is used in the Russian military system:
| S.No. | Color Code Tips | Bullet Types |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Black and Red | Armour piercing/incendiary |
| 2. | Red | Incendiary |
| 3. | Violet and Red | Armour piercing/incendiary/tracer |
| 4. | Violet | Armour piercing/incendiary/tracer |
| 5. | Green | Tracer |
| 6. | White | Mild Steel Bullet Core |
• Armor-Piercing Bullets: Design to penetrate either body armor or vehicle armor. They usually have hard cores made of steel or tungsten carbide.
• Incendiary Bullets: Have an incendiary material in the tip which on striking the surface, ignites the higher explosive
• Tracer Bullets: Have a small pyrotechnic charge in their base which traces its path.
Color Coding System of Bullets in China
Before 1967, China and Russia uses the same system of color coding for their bullets ammunitions. But after 1967, China adopted new color codes for their bullets.
| Color Code Tips | Bullet Types |
|---|---|
| Black and Red | Armour piercing/incendiary (pre-1967) |
| Black | Armour piercing/incendiary (post-1967) |
| Violet and Red | Armour piercing/incendiary/tracer (pre-1967) |
| Violet | Armour piercing/incendiary/tracer (post-1967) |
| Red | Incendiary |
| Green | Tracer |
| White | Mild Steel Bullet Core (pre-1967) |
Israel System of Color Coding of Bullets
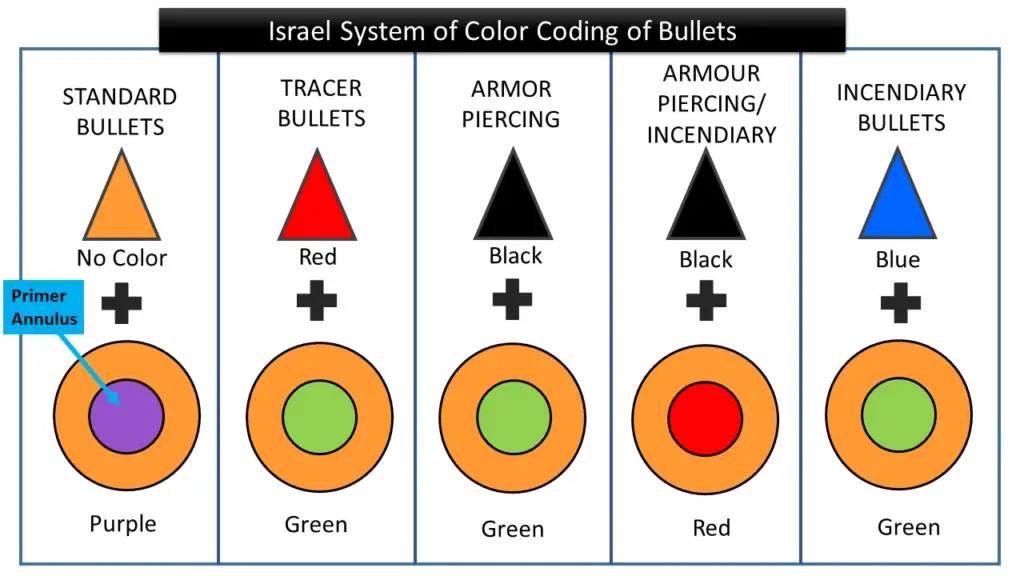
The following table states the color coding system of Israel for bullets that uses both the primer annulus and bullet tip coloring.
| Bullet Types | Bullet Tip Color | Primer Annulus Color |
|---|---|---|
| Ball | None | Purple |
| Tracer | Red | Green |
| Armour piercing | Black | Green |
| Armour piercing/incendiary | Black | Red |
| Incendiary | Blue | Green |
• Primer Annulus is the ring-like circular space between the top of the primer and the primer pocket on the base of a cartridge.
Color Coding Tips System for USA, UK, & Other NATO Countries
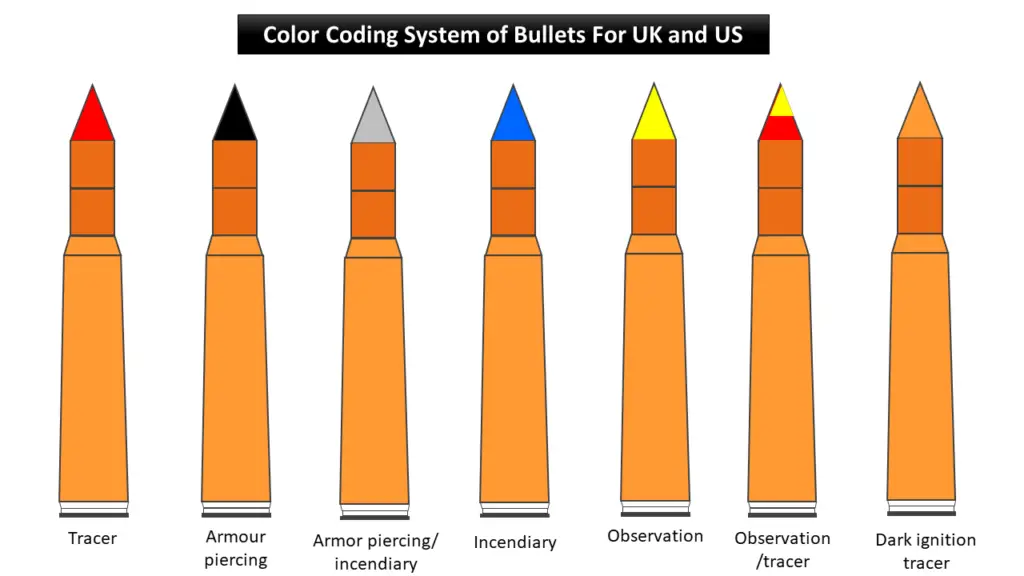
All NATO countries follow the same color-coding system for their bullet ammunitions, listed as:
| Color Code Tips | Bullet Types |
|---|---|
| Red | Tracer |
| Black | Armor-piercing |
| Silver | Armor-piercing/incendiary |
| Green | Steel core for better penetration against hard targets |
| Blue | Incendiary |
| Yellow | Observation (a bright flash & smoke on impact) |
| Yellow-Red | Observation/tracer |
| Orange | Dark ignition tracer |
United Kingdom Colour Coding System Prior to NATO
Before being a part of NATO in1955, the UK had a different coloring schema for their bullet ammunitions:
A. Color Coding System of UK Using Primer Annulus (Prior to NATO)
| Coloring Codes on Primer Annulus | Bullet Types |
|---|---|
| Purple | Ball or Short Range practice |
| Green | Armour piercing |
| Red | Tracer |
| Blue | Incendiary |
| Yellow | Proof (high-pressure cartridge) |
| Black | Observation (a bright flash & smoke on impact) |
| Orange | Some explosive rounds |
| Clear | Blank |
B. Color Coding System of UK Using Bullet tip (Prior to NATO)
| Color-Coded Tips | Bullet Type |
|---|---|
| Blue | Incendiary |
| Black | Observation |
| Green | Armour & semi-armor piercing |
| White | Short-range tracer (Day tracer) |
| Grey | Dark ignition tracer |
| Red | Long-range tracer |
| Violet | Experimental ammunition |
United States Color Coding System for Bullets
A. United States Color Coding System using Bullet Varnishes
| Color Code | Bullet Types |
|---|---|
| Red tip silver band | Armour piercing/incendiary/tracer |
| Yellow tip red band | Observation/tracer |
| Brown Tip | Tracer |
| Light blue tip | Incendiary |
B. United States Color Coding System Based on Firearms
| Special Firearms | Bullet Types |
|---|---|
| 0.50″ Browning machine gun | NATO Code plus |
| 0.30″ Carbine and 0.45′ ACP (Automatic Colt Pistol) | Red tip for tracer |
| 7.62 × 51mm | Same as NATO codes |
Color-Coded Bullet System in Warsaw Pact Countries
The following are the color codes that are currently employed in Warsaw pact countries:
| Color Code | Bullet Types |
|---|---|
| Yellow | Heavy ball |
| Silver | Light ball |
| Green | Tracer |
| Black | Armour piercing |
| Black/red | Armour piercing/incendiary (now obsolete) |
| Black/yellow | Armour piercing/incendiary (current) |
| Black/green | Reduced velocity for silenced weapons |
| Purple/red | Armour piercing/incendiary/tracer |
| Red | Incendiary/tracer |
General FAQ
What is the color code for the 5.56 bullet tip?
There are various types of color tips for 5.56/ .223 Rem but the most common color is a green-tip bullet that has a hardened steel core that serves better penetration against hard objects. Even a US civilian can acquire some by federal means.
What do different color tips on the bullet signify?
Green and black tips signify armor-piercing strength, orange, and red tip signify a tracer, blue bullet tip indicates incendiary bullets and yellow ammunition tips indicate observational bullets.
What does Blue tip on bullet mean?
A blue tip bullet in NATO countries like US and UK indicates incendiary bullets that burn rapidly or have high explosive incendiary. Modern blue-tip bullets are intended for armor penetration and then explode.
What is yellow tip ammo?
Yellow tip ammo is observation ammunition with an unhardened steel core that flakes out a bright flash and smoke on impact. They are commonly used for studying the impact or testing of firearms.
Reference:
- Handbook of Firearm and Ballistics by Brain J. Heard
- British Military Small Arms Ammo [link]
- FAS Military Analysis Network [link]
Continue Reading:
- Forensic Rulers and Scales: Types, Characteristics, and Uses
- Forensic Photography & Scales: How To Use Them Effectively With Examples

FR Author Group at ForensicReader is a team of Forensic experts and scholars having B.Sc, M.Sc, or Doctorate( Ph.D.) degrees in Forensic Science. We published on topics on fingerprints, questioned documents, forensic medicine, toxicology, physical evidence, and related case studies. Know More.
